Optical properties of the cylindrical mirror
Release time:
2024-03-06 09:43
Source:
1. An introduction to the cylindrical mirror
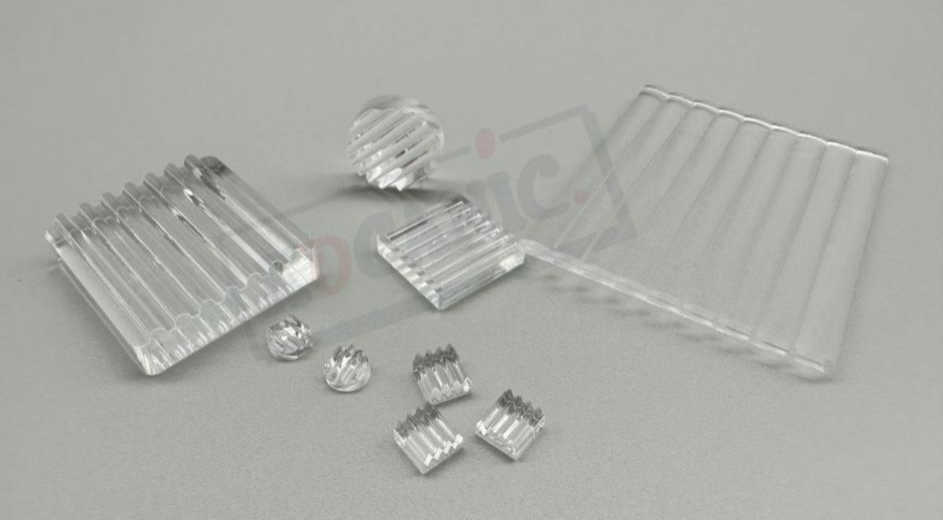
The cylindrical mirror belongs to the non-spherical lens, which can effectively reduce the spherical difference and color difference by design. The cylindrical mirror is divided into flat convex cylindrical lens, flat concave cylindrical lens, double convex cylindrical lens, double concave cylindrical lens, meniscus cylindrical lens, column cross cylindrical mirror and special shape cylindrical lens. With a one-dimensional amplification function.
Display of cylindrical mirror products:

2. The imaging principle of a cylindrical mirror
Because the special shape of the cylindrical mirror leads to the dislocation of light reflection, the figure on the plane will deform. The deformed flat image was projected onto the cylindrical mirror, which was deformed again. When the light is reflected through the cylindrical mirror, it will focus to the focus or disperse from the virtual focus. When the parallel beam enters, the light will be focused into a straight line by the cylindrical mirror. When non-parallel beams are incident, the imaging results vary depending to the incident angle.
Cylinder mirror light path display diagram:
Single convex:
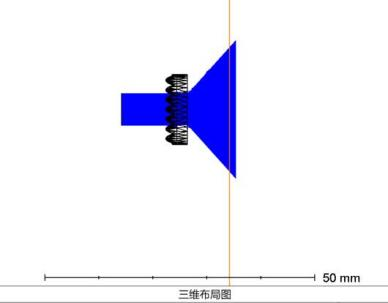
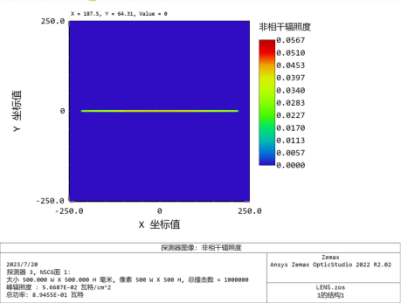
biconvex:
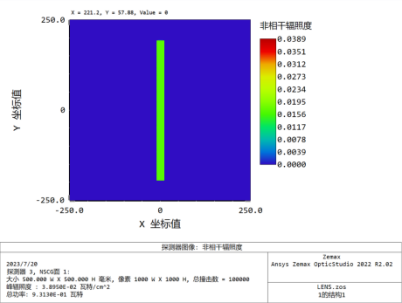
3. Column mirror gap analysis and comparison:
Take a product designed by a customer as an example, using a gap 0.3mm, 0.2mm, 0.1mm, 0.005mm, 0.002mm as an analysis.
1、The lens gap is 0.3mm: when the light is illuminated, the gap is large, the uniformity of the light spot is poor, and a bright focus will appear in the center.
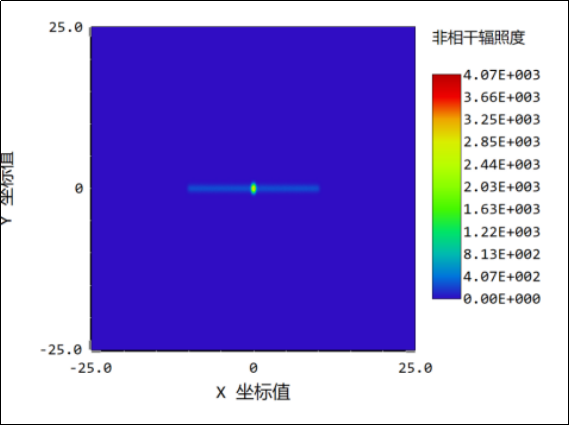
2、The lens gap is 0.2mm: when the light is illuminated, the gap is narrowed 1.5 times, the uniformity of light spot is improved, and the central focus and linear light spot are more obvious.
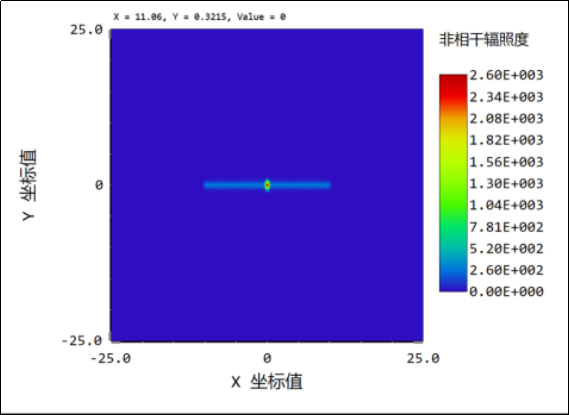
3. The lens gap is 0.1mm: when the light is illuminated on the gap, the gap is narrowed by 3 times, the uniformity of the light spot is further improved, the linear light spot is significant, and the central focus begins to weaken.
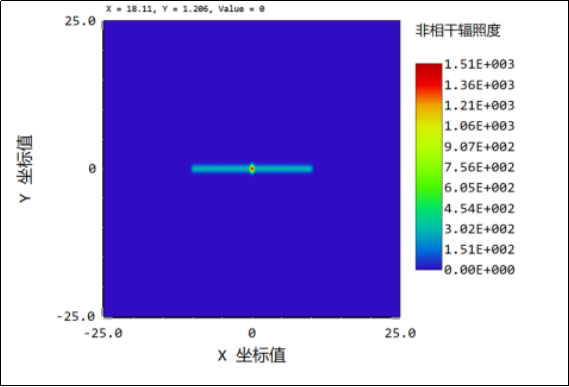
4. The lens gap is 0.005mm: when the light is illuminated, the gap is narrowed 60 times, the uniformity of the spot tends to be better, the central focus still exists, but the impact on the spot of light is small.
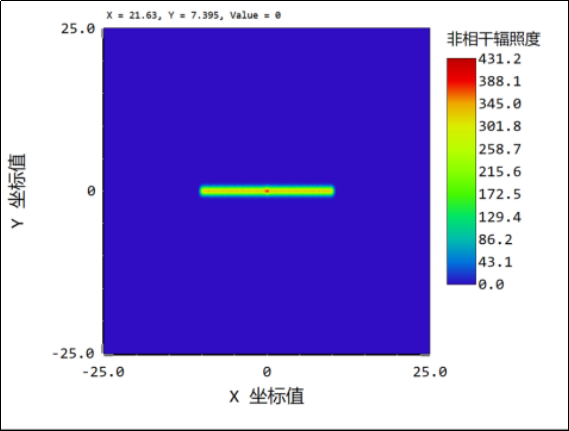
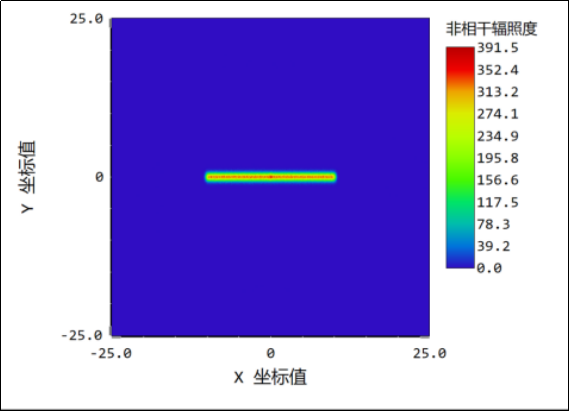
5、the lens gap is 0.002mm: when the light is illuminated, the gap is narrowed 150 times, the gap close to the ideal state is 0, the light spot uniformity is good, the middle focus is basically disappeared, negligible.
4. Column mirror imaging formula:
When the cylindrical mirror acts as the laser line generator, we can calculate the focal length by using the radius formula of the input beam:
2/d=effective focal length⋅tan( 2)
The divergence angle can be calculated by the required line length (x) and the working distance (L):
θ=2⋅tan-1 X/2L
The working distance can be calculated by the divergence angle (θ):
X=2⋅L⋅tan( 2/θ)
5. Use of a cylindrical
Cylindrical mirrors are widely used in high-precision tester and high-power lasers, long-distance line interferometer, linear detector illumination, barcode scanning, holographic illumination, optical information processing, computer and so on. Optical cylindrical mirrors are also widely used in strong laser systems and synchrotron radiation beam lines.
Recommended Articles
透镜,让世界更美好
2 minutes to understand the principle of the microstructure array lens
Microstructure array lenses are formed by nanoscale sub-lenses arranged in a certain order. Since each sublens in the microstructure array lens has an independent optical axis, a main optical axis is formed. Therefore, compared with the traditional compound eye single lens, the microstructure array lens has extremely high parallelism, and each sub-lens can transmit the light source independently of each other without interfering with each other.
What do you know about a spherical lens?
A spherical lens is a lens with a fixed radius of curvature on the surface of the lens inside the optical aperture. Spherical lenses are mainly divided into double convex lens, flat and concave lens, concave and convex lens, double concave lens, etc., which can be customized according to customer drawings or sample processing, to meet the different application needs of customers.
The difference between the Powell prism and the cylindrical array mirror
Powell prism: It is an optical nonspherical cylindrical mirror that allows the laser beam to preferably form a straight line with uniform density. Cylinder array mirror: Cylinder array mirror belongs to a kind of lens array. The core is the cylindrical microstructure distributed above, which can effectively reduce the spherical difference and chromatic difference by designing the aspherical surface shape, and has a one-dimensional amplification function.